
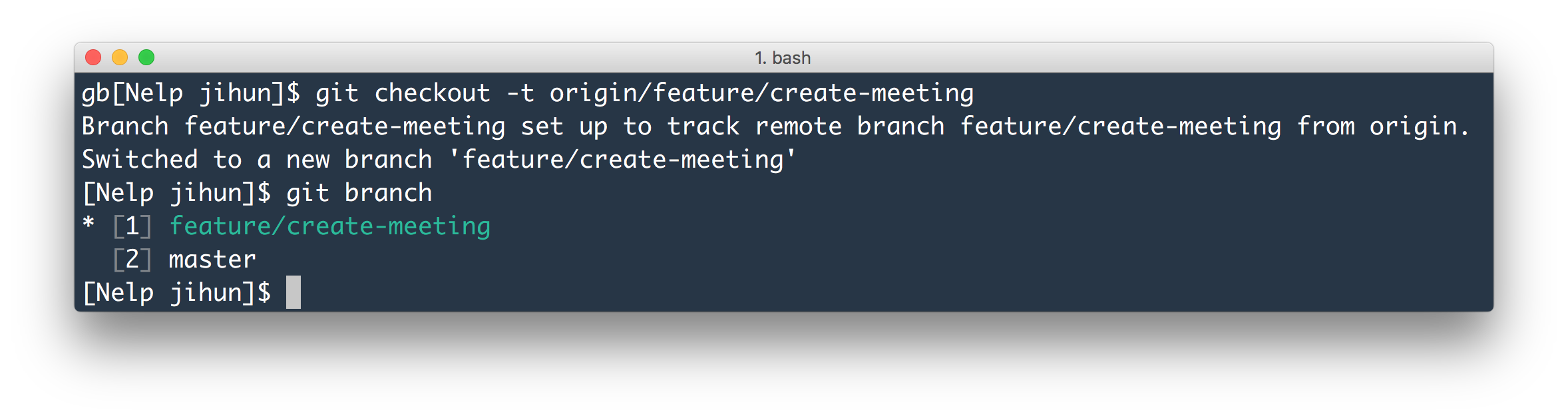
The documentation for handling branches using the console is great, but when I’ve been using TortoiseGit I’ve often felt confused and insecure when dealing with remote branches. This means that a branch is unique to each repository and the workflow when wanting to push a local branch to a remote repository, or the opposite, is a bit different. Git makes it really easy and fast to work with branches compared to many version control systems that aren’t distributed, but coming from the world of TFS or SubVersion where a branch is basically a physical directory that one can check in and check out in Git it’s pretty much just a pointer. This will also set up a tracking relationship between the local branch and the remote branch(upstream).As a user of TortoiseGit I’ve always been a bit confused when it comes to dealing with remote branches. By doing this we will be able to view the changes made by others and also modify them. We can check out a remote branch by first fetching it to our local repository and then creating a new local branch based on it. Collaborators will often share branches by pushing them to the remote repository. We can also see that our local branch feature has an upstream origin/feature by running the Git Branch command with the -vv flag.īranches are a great way to work on features and try out new things.Let's go back to our master branch and run the Git Checkout command with the -track option to create a new local branch based on the remote-tracking branch.But we can view the commit history by using the Git Log command. As shown below, our HEAD gets detached and we cannot make new changes without creating a new branch. Let's first try to check out the remote-tracking branch directly.We can view the remote branches by running the Git Branch command with the -r flag.Make sure you have set up the remote connection using the Git Remote Add command.

First, we will use the Git Fetch command to fetch all the branches from the remote. Suppose, we want to check out a remote branch called the feature.We will also know whether our local branch is leading ahead or lagging behind the remote branch.Ĭonsider the following example to understand the above steps better. This will make it easier for us to push and pull changes between these branches. Note that this local branch will have the remote branch as its Upstream.We can view these commits and even add new ones. This local branch will have the same name and the commit history as the remote branch. We will use the Git Checkout command with the -track option to create a new local branch based on the remote-tracking branch that we fetched.We can directly switch to these remote-tracking branches, but we won't be able to make any changes to it as our repository will be in a detached HEAD state. Use the Git Branch command with the -r flag to view the remote-tracking branch names.We can either mention the name of the remote branch or fetch all the remote branches present in the remote repository. Use the Git Fetch command to fetch the remote branch that you want to checkout.Follow the steps below to check out a remote branch. To check out a remote branch we first need to fetch it from the remote repository and then create a new local branch based on the one that we just fetched. Git provides us with the powerful and versatile Git Checkout command that is capable of doing this. In Git terminology, checkout means to navigate or switch to a different branch.
#Git checkout remote branch how to
In this tutorial, we will learn how to check out a remote Git branch on our local repository.

We can view and make changes to these branches by working on them on our local repository. All of the developers will be contributing to the project and will be pushing branches to the remote repository. We work with remote repositories to collaborate with other developers on our team.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
